Higgs Hunting 2025
100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot Curie
IJCLab
 The origin of Electroweak symmetry breaking is one of the central topics of research in fundamental physics. The discovery of a Higgs boson at CERN on July 4th, 2012, following a hunt that spanned several decades and multiple colliders, changed the landscape of these investigations and provided key evidence for the Brout-Englert-Higgs mechanism of mass generation through the spontaneous breaking of Electroweak symmetry.
The origin of Electroweak symmetry breaking is one of the central topics of research in fundamental physics. The discovery of a Higgs boson at CERN on July 4th, 2012, following a hunt that spanned several decades and multiple colliders, changed the landscape of these investigations and provided key evidence for the Brout-Englert-Higgs mechanism of mass generation through the spontaneous breaking of Electroweak symmetry.
More than ten years later, the hunt goes on several fronts, in particular for:
- New physics through precision studies of the properties of the Higgs boson : in particular its mass, spin and couplings to other Standard Model particles.
- New production and decay modes, in particular in processes involving multiple Higgs bosons which provide key insight into the shape of the Higgs potential.
- New Higgs-like states and signals for physics beyond the Standard Model.
The 15th workshop of the « Higgs Hunting » series organized on July 15-17 2025 will present an overview of these topics, focusing in particular on new developments in the LHC Run-2 analyses, detailed studies of Higgs boson properties and possible deviations from Standard Model predictions. Highlights will also include a first look at LHC Run-3 analyses, prospects from studies at future colliders, and recent theoretical developments.
The workshop will be held in person in Orsay, for the first day, and Paris, for the two following days, to continue the Higgs Hunting tradition of lively discussions during and after the sessions. Remote participation will also be made possible for those unable to attend in person. No registration fees are asked for remote participation.
|
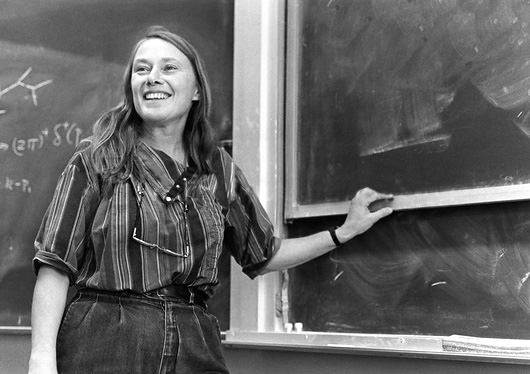 Mary K. Gaillard passed away on 23 May 2025. A major figure in particle theory, she made fundamental contributions to the establishment of the Standard Model. Notably, she achieved a successful determination of the charm quark mass from kaon decays; predicted three-jet events in e+ e- collisions, providing crucial evidence for the existence of gluons; and forecasted the bottom quark mass within the framework of unified theories. She also pioneered systematic studies of Higgs boson production and decay at particle colliders, sketching its first phenomenological profile that launched its experimental hunt. Beyond the Standard Model, Mary K. made numerous and invaluable contributions to Grand Unified Theories and supersymmetric theories, including work on proton decay, supersymmetry breaking, and effective supergravity theories derived from superstrings. The Higgs Hunting workshop was honored to welcome her in 2016 as the speaker for its traditional historical talk Mary K. Gaillard passed away on 23 May 2025. A major figure in particle theory, she made fundamental contributions to the establishment of the Standard Model. Notably, she achieved a successful determination of the charm quark mass from kaon decays; predicted three-jet events in e+ e- collisions, providing crucial evidence for the existence of gluons; and forecasted the bottom quark mass within the framework of unified theories. She also pioneered systematic studies of Higgs boson production and decay at particle colliders, sketching its first phenomenological profile that launched its experimental hunt. Beyond the Standard Model, Mary K. made numerous and invaluable contributions to Grand Unified Theories and supersymmetric theories, including work on proton decay, supersymmetry breaking, and effective supergravity theories derived from superstrings. The Higgs Hunting workshop was honored to welcome her in 2016 as the speaker for its traditional historical talkthan you can see in
Mary K. spent a substantial portion of her career in France and at CERN, from her doctoral studies in Orsay to the creation of the theoretical physics laboratory LAPTh in Annecy. The Higgs Hunting workshop extends its deepest condolences to her colleagues at the University of California, Berkeley, and to her family. |

 |
 |
 |
|
-
-
09:00
→
09:55
Registration (with coffee and croissants) 55m 100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot Curie
100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot Curie
IJCLab
IJCLab Orsay (Tuesday) & APC Paris (Wednesday & Thursday)140Montrer la salle sur la carte -
09:55
→
10:00
Prelude from the organizers 5m 100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot Curie
100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot Curie
IJCLab
IJCLab Orsay (Tuesday) & APC Paris (Wednesday & Thursday)140Montrer la salle sur la carte -
10:00
→
10:45
Plenary: Theory overview 100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot CuriePrésident de session: Nick Wardle (Imperial College)
-
10:00
Theory overview 45mOrateur: Thomas Gehrmann (Universität Zurich)
-
10:00
-
10:45
→
11:15
Topical talks: Part 1 100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot Curie
-
10:45
Measurements of the Higgs boson mass and width in CMS 12mOrateur: Neha Rawal (University of Florida)Abstract Ever since the discovery of the Higgs boson by the ATLAS and CMS Collaborations at LHC in 2012, precision measurements of its properties have been performed intensively. This is crucial for further understanding the Standard Model (SM) as well as to search for beyond the SM physics. This presentation focuses on precision measurements of the Higgs boson mass and total decay width performed using proton-proton collision data collected by the CMS detector during Run 2 of the LHC. It includes analysis strategies and techniques for precise and accurate measurement of the mass and discusses direct measurement of the width from the Higgs resonance peak. We also highlight studies on indirect width measurements which provide a better constraint on its value compared to direct measurements which are limited by the detector resolution.
-
10:57
Constraining the Higgs boson width from Higgs-top Yukawa coupling at the ATLAS experiment 12mOrateur: Yangfan Zhang (University of Science and Technology of China)
-
10:45
-
11:15
→
13:00
Plenary: Higgs boson properties and couplings 100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot CuriePrésident de session: Nick Wardle (Imperial College)
-
11:15
Higgs boson property measurements (mass, width, CP) - CMS 15mOrateur: Amrutha Krishna (Northeastern University)
-
11:30
Higgs boson property measurements (mass, width, CP) - ATLAS 15mOrateur: Elise Le Boulicaut (Yale University)
-
11:45
Higgs boson coupling measurements - CMS 15mOrateur: Walaa Elmetenawee (Universita e INFN, Bari)
-
12:00
Higgs boson coupling measurements - ATLAS 15mOrateur: Fábio Lucio Alves (Nanjing University)
-
12:15
Higgs boson properties and couplings - 3-slide overview 5mOrateur: Nicholas Wardle (Imperial College London)
-
12:20
Discussion of present status and prospects for coupling and property measurements 40m
-
11:15
-
13:00
→
14:30
Lunch 1h 30m Bures cafeteria (Orsay)
Bures cafeteria
Orsay
-
14:30
→
14:55
Topical talks: Part 2 100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot CuriePrésident de session: Roberto SALERNO (LLR)
-
14:30
Searches for Higgs coupling to charm quarks at the ATLAS experiment 12mOrateur: Greta Brianti (Università di Trento)
-
14:42
Search for H→cc at the CMS experiment 12mOrateur: Angela Zaza (Univ. di Bari e Sez. dell'INFN)Abstract Probing the Higgs boson coupling to second generation quarks, still out of reach, is currently one of the most challenging goals of the CMS and ATLAS collaborations. The CMS collaboration carried out searches for the Higgs boson decay in a charm quark-antiquark pair with data collected during the Run-2 of the LHC (2016-2018), by exploring the Higgs boson associated production with a vector boson (VH) , the gluon fusion (ggF) and the associated production with a top quark-antiquark pair (ttH) production mechanisms. By combining the ttH and VH production mechanisms, CMS set the most stringent constraint to date on the Hcc Yukawa coupling modifier: |kc| < 3.5 (2.7). An overview on the searches for H→cc carried out by the CMS collaboration will be presented in this contribution.
-
14:30
-
14:55
→
15:25
Plenary: The Higgs boson self-coupling and the electroweak phase transition 100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot CuriePrésident de session: Roberto SALERNO (LLR)
-
14:55
Footprints of the Electroweak Phase Transition at Colliders 30mOrateur: Oleksii Matsedonskyi (Cambridge University)
-
14:55
-
15:25
→
16:30
Plenary: Higgs boson self-coupling and Di-Higgs production 100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot CuriePrésident de session: Roberto SALERNO (LLR)
-
15:25
Higgs boson self-coupling and Di-Higgs production - ATLAS 15mOrateurs: Lorenzo Santi (CERN), Lorenzo santi (INFN - Roma1)
-
15:40
Higgs boson self-coupling and Di-Higgs production - CMS 15mOrateurs: Leonidas Paizanos (University of Cyprus), Leonidas Paizanos (University of Cyprus)
-
15:55
Higgs boson self-coupling and Di-Higgs production: 3-slide overview 5mOrateur: Roberto SALERNO (LLR)
-
16:00
Discussion of Higgs boson self-coupling and Di-Higgs production 30m
-
15:25
-
16:30
→
17:00
Coffee break 30m 100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot Curie
100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot Curie
IJCLab
IJCLab Orsay (Tuesday) & APC Paris (Wednesday & Thursday)140Montrer la salle sur la carte -
17:00
→
17:30
Plenary: Parton distribution functions 100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot CuriePrésident de session: Ben Kilminster (Universität Zürich)
-
17:00
PDFs for Higgs boson processes at the LHC 30mOrateur: Juan Rojo (Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam)
-
17:00
-
17:30
→
18:10
Topical talks: Part 3 100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot CuriePrésident de session: Ben Kilminster (Universität Zürich)
-
17:30
Model-independent differential measurement in H→WW at the CMS experiment 12mOrateur: Benedetta Camaiani (Univ. di Firenze e Sez. dell'INFN)Abstract We present the differential measurement of H+jets in the WW decay channel using full run 2 CMS data. The measurements presented probe the CP nature of the Higgs boson couplings. A novel approach was used, exploiting adversarial neural network, to minimize model dependency of the measurement and allow reinterpretability. Constraints on several Wilson coefficients are also derived.
-
17:42
Naturalness, near-criticality and future colliders 12mOrateur: Víctor Enguita Vileta (Instituto de Física Teórica (IFT) UAM-CSIC)
-
17:54
An Isotropic Prescription for Constructing the SMEFT in Normal Coordinates to Simplify Amplitude Computations 15mOrateur: Mia West (University of Florida)
Geometry provides us with a convenient interpretation of field-redefinition invariance for amplitudes and has many useful properties. For instance, it directs us towards Riemann Normal Coordinates (RNC) as an ideal choice of field-redefinition to compute amplitudes. It has been shown in the Higgs Effective Field Theory (EFT) assuming custodial symmetry & in the high-energy limit in RNC there are distinct kinematics for each Feynman graph. Redefining the Lagrangian in these coordinates appears to generate a reduced set of Feynman graphs which still sum to the correct amplitude. This property also holds in the Standard Model EFT (SMEFT) as a subset of HEFT. In this talk, we will demonstrate a prescription to construct the SMEFT in RNC around the symmetric point using isotropy, applicable to all orders in the SMEFT expansion. Then, breaking electroweak symmetry corresponds to traversing a geodesic to the vacuum and re-establishing RNC in terms of isotropic properties of the symmetric point. We argue that this prescription is simpler compared to the usual recursive method to construct RNC.
-
17:30
-
18:10
→
19:00
Historical talk 100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot Curie
100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot Curie
IJCLab
IJCLab Orsay (Tuesday) & APC Paris (Wednesday & Thursday)140Montrer la salle sur la cartePrésident de session: Ben Kilminster (Universität Zürich)-
18:10
Mysterious Neutrinos 50mOrateur: Pierre Ramond (University of Florida)
-
18:10
-
19:00
→
20:30
Welcome cocktail 1h 30m 100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot Curie
100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot Curie
IJCLab
IJCLab Orsay (Tuesday) & APC Paris (Wednesday & Thursday)140Montrer la salle sur la carte
-
09:00
→
09:55
-
-
09:25
→
10:00
Coffee 35m LPNHE Paris
LPNHE Paris
-
10:00
→
10:25
Plenary: CMS Joker talk Amphithéâtre Charpak (LPNHE Paris)
Amphithéâtre Charpak
LPNHE Paris
Président de session: Sven Heinemeyer (IFT/IFCA (CSIC))-
10:00
CMS Joker talk: Search for anomalous Higgs couplings with H→γγ decays 25mOrateur: Federica De Riggi (Univ. di Roma I e Sez. dell'INFN)
-
10:00
-
10:25
→
10:40
Topical talks: Part 4 Amphithéâtre Charpak (LPNHE Paris)
Amphithéâtre Charpak
LPNHE Paris
-
10:25
Search for CP violating effects in HWW vertex in WH production channel in 13 TeV pp collisions with the ATLAS detector 12mOrateur: Ricardo Barrue (LIP - Laboratório de Instrumentação e Física Experimental de Partículas)
-
10:25
-
10:40
→
11:55
Plenary: BSM H(125) aspects and searches for new scalar bosons Amphithéâtre Charpak (LPNHE Paris)
Amphithéâtre Charpak
LPNHE Paris
Président de session: Sven Heinemeyer (IFT/IFCA (CSIC))-
10:40
BSM H(125) aspects and searches for new scalar bosons - CMS 20mOrateur: Siddhesh Sawant (Baylor University)
-
11:00
BSM H(125) aspects and searches for new scalar bosons - ATLAS 20mOrateur: Eleni Skorda (University of Birmingham)
-
11:20
BSM H(125) aspects and searches for new scalar bosons: 3-slide overview 5mOrateur: Sven Heinemeyer (IFT/IFCA (CSIC))
-
11:25
Discussion of BSM H(125) aspects and searches for new scalar bosons 30m
-
10:40
-
11:55
→
13:05
Lunch buffet 1h 10m LPNHE Paris
LPNHE Paris
-
13:05
→
13:50
Plenary: Analysis methods Amphithéâtre Charpak (LPNHE Paris)
Amphithéâtre Charpak
LPNHE Paris
Président de session: Julie Malcles (CEA-Saclay/Irfu, Université Paris-Saclay)-
13:05
Analysis methods - CMS 15mOrateur: Maria Mazza (Florida State University)
-
13:20
Analysis methods - ATLAS 15mOrateur: Andrea Sciandra (UCSC)
-
13:35
Analysis methods: 3-slide summary 5mOrateur: Julie Malcles (CEA-Saclay/Irfu, Université Paris-Saclay)
-
13:40
Discussion of analysis methods 10m
-
13:05
-
13:50
→
14:45
Topical talks: Part 5 Amphithéâtre Charpak (LPNHE Paris)
Amphithéâtre Charpak
LPNHE Paris
Président de session: Julie Malcles (CEA-Saclay/Irfu, Université Paris-Saclay)-
13:50
Gauge-Higgs Unification and Symmetry Breaking: application to 5D GUTs 12mOrateur: Wanda Isnard (IP2I Lyon)
-
14:02
Search for Higgs boson decays into a pair of pseudoscalar particles in the yytautau final state using pp collisions at \sqrt{s} = 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector 12mOrateur: Gadi Ninio (Tel Aviv University)
-
14:14
Flavour Deconstructing the Composite Higgs 12mOrateur: Marko Pesut (University of Zurich)
Abstract: In the first part of the talk, we will introduce the main model building ideas (flavour non-universality and Higgs compositeness) that are central to our model, as well as the theoretical and experimental motivations for exploring these BSM avenues. In the second part of the talk, we present a flavour non-universal extension of the Standard Model combined with the idea of Higgs compositeness. At the TeV scale, the electroweak gauge symmetry is assumed to act in a non-universal manner on light- and third-generation fermions, while the Higgs emerges as a pseudo Nambu-Goldstone boson of a spontaneously broken global symmetry. The flavour deconstruction implies that the couplings of the light families to the composite sector are suppressed by powers of a heavy mass scale, explaining the flavour puzzle. We present a detailed analysis of the radiatively generated Higgs potential, showing how this intrinsically-flavoured framework has the ingredients to justify the unavoidable tuning in the Higgs potential necessary to separate electroweak and composite scales. The model is compatible with current experimental bounds and predicts new states at the TeV scale, which are within the reach of near future experimental searches.
Arxiv: 2407.10950 -
14:26
Search for a standard model-like Higgs boson in the mass range between 70 and 110 GeV in the diphoton final state in proton-proton collisions with CMS at √s=13 GeV 12mOrateur: Benjamin Massoteau (IPN, IN2P3-CNRS, UCB Lyon 1)Abstract The results of a search for a standard model-like Higgs boson decaying into two photons in the mass range between 70 and 110 GeV are presented. The analysis uses the data set collected with the CMS experiment in proton-proton collisions from Run 2 at √s=13 TeV and part of the data set from Run 3, at √s=13.6 TeV. The expected and observed 95% confidence level upper limits on the product of the cross section and branching fraction for decays of an additional Higgs boson into two photons are presented.
-
13:50
-
14:45
→
15:15
Plenary: VBS Amphithéâtre Charpak (LPNHE Paris)
Amphithéâtre Charpak
LPNHE Paris
Président de session: Pamela Ferrari (Radboud University Nijmegen & Nikhef)-
14:45
Vector boson scattering and the Higgs boson 30mOrateur: Mathieu Pellen (University of Freiburg)
-
14:45
-
15:15
→
15:45
Coffee break 30m LPNHE Paris
LPNHE Paris
-
15:45
→
17:10
Plenary: Effective field theories Amphithéâtre Charpak (LPNHE Paris)
Amphithéâtre Charpak
LPNHE Paris
Président de session: Pamela Ferrari (Radboud University Nijmegen & Nikhef)-
15:45
Effective field theories - theory overview 20mOrateur: Jose SANTIAGO PEREZ (Universidad de Granada)
-
16:05
Effective field theories - ATLAS 15mOrateur: Elena Mazzeo (CERN)
-
16:20
Effective field theories - CMS 15mOrateur: Suman Chatterjee (Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron (DESY))
-
16:35
Effective field theories: 3-slide overview 5mOrateur: Pamela Ferrari (Radboud University Nijmegen & Nikhef)
-
16:40
Discussion of EFT interpretations 30m
-
15:45
-
17:10
→
17:40
Topical talks: Part 6 Amphithéâtre Charpak (APC Paris)
Amphithéâtre Charpak
APC Paris
Président de session: Pamela Ferrari (Radboud University Nijmegen & Nikhef)- 17:10
-
17:25
The Higgs meets the SMEFT at higher orders 15mOrateur: Dr Stefano Di Noi (KIT (ITP))
-
17:40
→
18:20
Plenary: Vision talk Amphithéâtre Charpak (LPNHE PAaris)
Amphithéâtre Charpak
LPNHE PAaris
Président de session: Pamela Ferrari (Radboud University Nijmegen & Nikhef)-
17:40
Vision talk: Higgs physics and Early Universe cosmology 35mOrateur: Alfredo URBANO (Sapienza University of Rome and INFN)
-
17:40
-
18:59
→
19:00
Dinner information 1m 100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot Curie
100/-1-A900 - Auditorium Joliot Curie
IJCLab
IJCLab Orsay (Tuesday) & APC Paris (Wednesday & Thursday)140Montrer la salle sur la carte -
19:00
→
23:00
Dinner 4h "Capitaine Fracasse" river barge
"Capitaine Fracasse" river barge
Departure from "Ile aux cygnes" (RER station "Champ de Mars Tour Eiffel", métro station "Bir-Hakeim")
Boarding at 20:15, return at 23:00
-
09:25
→
10:00
-
-
09:30
→
10:00
Coffee 30m LPNHE Paris
LPNHE Paris
-
10:00
→
10:25
Plenary: ATLAS Joker talk Amphithéâtre Charpak (LPNHE Paris)
Amphithéâtre Charpak
LPNHE Paris
Président de session: Karl Jakobs (University of Freiburg))-
10:00
ATLAS Joker talk: Recent results of searches for Higgs boson decays with the ATLAS detector 25mOrateur: Stefano Manzoni (CERN)
-
10:00
-
10:25
→
12:45
Plenary: Higgs physics within the European strategy update Amphithéâtre Charpak (LPNHE Paris)
Amphithéâtre Charpak
LPNHE Paris
Président de session: Karl Jakobs (University of Freiburg)-
10:25
Challenges in Theory Predictions 25mOrateur: Federico Buccioni (TUM)
-
10:50
Accelerators overview 25mOrateur: Frank Zimmermann (CERN)
-
11:15
Overview of the ESPPU strategy for Higgs and Electroweak physics and introduction to the discussion 20mOrateurs: Gregorio BERNARDI (APC-Paris CNRS/IN2P3), gregorio bernardi (lpnhe)
-
11:35
Discussion 1h 10m
-
10:25
-
12:45
→
14:15
Lunch buffet 1h 30m LPNHE Paris
LPNHE Paris
-
14:15
→
14:45
Plenary: Toponium Amphithéâtre Charpak (LPNHE Paris)
Amphithéâtre Charpak
LPNHE Paris
Président de session: Florencia Canelli (Universität Zürich)-
14:15
Toponium formation at the Large Hadron Collider 30mOrateur: Prof. Benjamin Fuks (LPTHE / Sorbonne U.)
-
14:15
-
14:45
→
16:15
Plenary: Concluding talks Amphithéâtre Charpak (LPNHE Paris)
Amphithéâtre Charpak
LPNHE Paris
Président de session: Florencia Canelli (Universität Zürich)-
14:45
Theory concluding talk 45mOrateur: Gavin Salam (University of Oxford, Department of Physics and All Souls College)
-
15:30
Experimental concluding talk 45mOrateur: Maria Cepeda (CIEMAT)
-
14:45
-
16:15
→
17:15
Farewell coffee 1h LPNHE Paris
LPNHE Paris
-
09:30
→
10:00
